What is 2D IC Package Substrate?
2D IC Package firm and 2D IC package substrate manufacturer. We use advanced Msap and Sap technology, High multilayer interconnection substrates from 4 to 20 layers. and we also do the 2D IC Package service.
A 2D IC package substrate is a component used in the construction of integrated circuits (ICs) that are packaged in a two-dimensional format. It serves as a platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic components within the IC package.
The substrate is typically made of a thin, flat material such as silicon, glass, or a ceramic material like alumina. It features a network of conductive traces that provide electrical connections between the different components, such as the IC die, passive components, and external pins or leads.
In addition to providing electrical connections, the substrate also helps to dissipate heat generated by the ICs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. It may include features such as vias (vertical interconnect access) for routing signals between different layers, as well as thermal management structures like heat spreaders or heat sinks.
Overall, the 2D IC package substrate plays a crucial role in the assembly and functioning of integrated circuits, providing both electrical connectivity and thermal management capabilities.
What are the functions of 2D IC Package Substrate?
2D IC Package Substrate serves several functions, including:
Electrical connectivity: The substrate provides a platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic components within the IC package. It features a network of conductive traces that facilitate electrical connections between the different components, such as the IC die, passive components, and external pins or leads.
Signal routing: The substrate includes features such as vias (vertical interconnect access) for routing signals between different layers. This ensures that signals can be efficiently transmitted between the various components within the IC package.
Heat dissipation: The substrate helps to dissipate heat generated by the ICs during operation. It may include thermal management structures such as heat spreaders or heat sinks, which help to distribute and dissipate heat effectively, ensuring optimal performance and reliability of the ICs.
Mechanical support: The substrate provides mechanical support for the IC components, helping to ensure their stability and integrity within the package. It helps to protect the components from mechanical stress and vibrations, which could otherwise affect their performance and longevity.
Overall, the functions of 2D IC Package Substrate are crucial for the assembly, functioning, and reliability of integrated circuits, providing electrical connectivity, signal routing, heat dissipation, and mechanical support for the various components within the IC package.
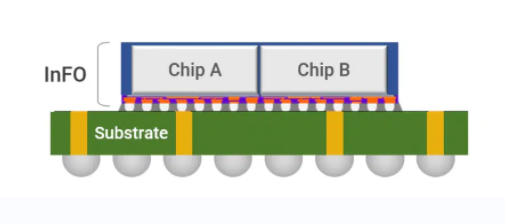
2D IC Package Substrate
What are the different types of 2D IC Package Substrate?
There are several different types of 2D IC package substrates, each with its own characteristics and applications. Some common types include:
Organic substrates: These substrates are made of organic materials such as epoxy resin or polyimide. They are lightweight, cost-effective, and offer good electrical performance. Organic substrates are commonly used in consumer electronics and mobile devices.
Ceramic substrates: Ceramic substrates are made of materials like alumina (aluminum oxide) or aluminum nitride. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-power applications and environments with high temperatures.
Silicon substrates: Silicon substrates are made of silicon wafers and are commonly used in advanced packaging technologies such as system-in-package (SiP) and fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP). They offer high integration density and electrical performance but can be more expensive than organic or ceramic substrates.
Glass substrates: Glass substrates are used in specialized applications such as microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and optoelectronic devices. They offer good optical properties, low thermal expansion, and compatibility with high-temperature processes.
Metal substrates: Metal substrates are made of materials like copper or aluminum and are often used in high-power applications such as power modules and LED packages. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and can efficiently dissipate heat generated by the ICs.
These are just a few examples of the different types of 2D IC package substrates available, each offering unique properties and advantages for specific applications.
What is the relationship between 2D IC Package Substrate and IC packaging?
The relationship between 2D IC package substrate and IC packaging is that the substrate is an integral part of the IC packaging process. IC packaging involves enclosing the semiconductor die (IC) in a protective housing or package and providing electrical connections to the outside world. The substrate serves as the foundation upon which the IC die and other components are mounted and interconnected within the package.
The substrate plays a crucial role in the assembly, functioning, and reliability of the packaged IC. It provides electrical connectivity between the IC die, passive components, and external pins or leads through a network of conductive traces. Additionally, the substrate facilitates signal routing between different layers within the package, ensuring efficient transmission of signals between the various components.
Furthermore, the substrate helps to dissipate heat generated by the ICs during operation, thereby ensuring optimal performance and reliability. It may include thermal management structures such as heat spreaders or heat sinks, which help to distribute and dissipate heat effectively.
Overall, the 2D IC package substrate is an essential component of IC packaging, providing electrical connectivity, signal routing, heat dissipation, and mechanical support for the various components within the package. It contributes significantly to the performance, functionality, and longevity of the packaged IC.
How does 2D IC Package Substrate differ from PCB?
2D IC package substrate and printed circuit board (PCB) are both used in electronic devices, but they serve different purposes and have different characteristics. Here are some key differences between the two:
Purpose:
2D IC package substrate: The main purpose of a 2D IC package substrate is to provide a platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic components within an integrated circuit (IC) package. It serves as a foundation for the IC die, passive components, and external pins or leads.
PCB: A PCB is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks, and pads. It provides a platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits in a wide range of electronic devices.
Construction:
2D IC package substrate: The substrate is typically made of a thin, flat material such as silicon, glass, or ceramic. It features a network of conductive traces that provide electrical connections between the different components within the IC package.
PCB: A PCB is typically made of a non-conductive substrate material, such as fiberglass, epoxy resin, or phenolic resin, with conductive copper traces and pads etched or printed onto its surface. The conductive pathways on the PCB form the electrical connections between the components mounted on it.
Complexity:
2D IC package substrate: The design and fabrication of 2D IC package substrates are highly specialized and tailored to the specific requirements of the IC packaging process. They are often more complex and tightly integrated than standard PCBs, with features such as vias for signal routing and thermal management structures.
PCB: PCBs come in various sizes and complexities, ranging from simple single-layer boards to complex multi-layer boards with intricate routing and dense component placement. They are used in a wide range of electronic devices, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment.
Overall, while both 2D IC package substrates and PCBs are used in electronic devices, they serve different purposes and have different characteristics. 2D IC package substrates are specialized components used specifically in IC packaging processes, while PCBs are used for general electronic interconnection and support applications.
What are the structure and production technology of 2D IC Package Substrate?
The structure and production technology of 2D IC Package Substrate can vary depending on the specific requirements of the application and the materials used. However, here is a general overview of the typical structure and production process:
Structure:
Substrate material: The substrate is typically made of a thin, flat material such as silicon, glass, or ceramic. The choice of material depends on factors such as thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical properties.
Conductive traces: The substrate features a network of conductive traces that provide electrical connections between the different components within the IC package. These traces are typically made of metals such as copper or aluminum and are patterned onto the substrate using techniques such as etching or deposition.
Vias: Vias are vertical interconnects that allow signals to pass between different layers of the substrate. They are typically formed by drilling or etching holes through the substrate and filling them with conductive material.
Thermal management structures: The substrate may include thermal management structures such as heat spreaders, heat sinks, or thermal vias to help dissipate heat generated by the ICs during operation.
Production technology:
Substrate fabrication: The substrate is fabricated using techniques such as wafer dicing, laser cutting, or chemical etching to achieve the desired dimensions and features.
Metallization: Conductive traces are patterned onto the substrate using techniques such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or electroplating. These techniques deposit a thin layer of metal onto the substrate surface, which is then patterned and etched to form the desired traces.
Via formation: Vias are formed by drilling or etching holes through the substrate and filling them with conductive material such as copper or tungsten. This process may involve multiple steps, including substrate drilling, via filling, and planarization to ensure a smooth surface.
Thermal management: Thermal management structures such as heat spreaders or heat sinks may be integrated into the substrate during fabrication using techniques such as bonding or deposition.
Overall, the production technology of 2D IC Package Substrate involves a combination of substrate fabrication, metallization, via formation, and thermal management techniques to achieve the desired structure and performance characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a 2D IC Package Substrate?
A 2D IC Package Substrate is a component used in the construction of integrated circuits (ICs) that are packaged in a two-dimensional format. It serves as a platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic components within the IC package.
What are the functions of a 2D IC Package Substrate?
The functions of a 2D IC Package Substrate include providing electrical connectivity between components, facilitating signal routing, dissipating heat generated by the ICs, and providing mechanical support for the components within the IC package.
How does a 2D IC Package Substrate differ from a PCB?
While both 2D IC Package Substrate and printed circuit boards (PCBs) are used in electronic devices, they serve different purposes and have different characteristics. 2D IC Package Substrate is specialized for IC packaging processes, while PCBs are used for general electronic interconnection and support applications.
What are the different types of 2D IC Package Substrate?
Common types of 2D IC Package Substrate include organic substrates, ceramic substrates, silicon substrates, glass substrates, and metal substrates. Each type has unique properties and advantages for specific applications.
What is the relationship between 2D IC Package Substrate and IC packaging?
The 2D IC Package Substrate is an integral part of the IC packaging process, providing electrical connectivity, signal routing, heat dissipation, and mechanical support for the components within the IC package.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 2D IC Package Substrate is a critical component in the construction of integrated circuits (ICs) packaged in a two-dimensional format. It serves multiple functions, including providing electrical connectivity, facilitating signal routing, dissipating heat, and offering mechanical support for the components within the IC package.
The substrate comes in various types, such as organic, ceramic, silicon, glass, and metal substrates, each with unique properties and advantages suited for specific applications. Its production involves a combination of substrate fabrication, metallization, via formation, and thermal management techniques to achieve the desired structure and performance characteristics.
The relationship between the 2D IC Package Substrate and IC packaging is close, as the substrate is an integral part of the packaging process, contributing significantly to the performance, functionality, and reliability of the packaged IC.
Overall, the 2D IC Package Substrate plays a crucial role in the assembly, functioning, and longevity of integrated circuits, making it an essential component in various electronic devices and systems.
 Flip-Chip Package Substrate manufacturer
Flip-Chip Package Substrate manufacturer
